Highlights of some of our recent papers
Bardwell AJ, Paul, M, Yoneda KC, Andrade-Ludeña, MD, Nguyen OT, Fruman, DA and Bardwell L (2023)
The WW domain of IQGAP1 binds directly to the p110α catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase
Biochemical Journal (2023) 480 729–750 (cover article)
Background: IQGAP1 is a multidomain cancer-associated protein that serves as a scaffold protein for multiple signaling pathways. Identification of a binding partner for its WW domain has proven elusive, however, even though a cell-penetrating peptide derived from this domain has marked anti-tumor activity.
Results: We show that the WW domain of human IQGAP1 binds directly to the p110α catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). p110α is an oncogenic driver and the gene that encodes it (PIK3CA) is one of the most frequently mutated genes in human cancer.
Conclusion and Significance: These findings contribute to a more precise understanding of IQGAP1 mediated scaffolding, and of how IQGAP1-derived therapeutic peptides might inhibit tumorigenesis.
Bardwell AJ, Wu, B, Sarin KY, Waterman ML, Atwood SX, and Bardwell L (2022)
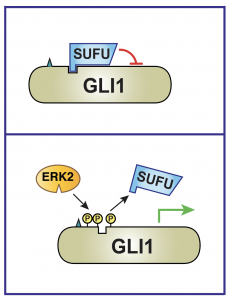
ERK2 MAP kinase regulates SUFU binding by multisite phosphoryaltion of GLI1
Life Science Alliance 5(11):e202101353 DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202101353
** Read the Press Release HERE **
Background: Crosstalk between the Hedgehog and MAPK signaling pathways occurs in several types of cancer and contributes to clinical resistance to Hedgehog pathway inhibitors. GLI1 is a transcription factor in the Hedgehog pathway, and SUFU is a negative regulator of GLI1.
Results: We show that MAPK-mediated phosphorylation of GLI1 on three residues near the SUFU-binding site results in a dramatic weakening of SUFU binding to this region, and a consequent relief of repression. This leads to an increase in GLI1-driven transcription of growth-promoting genes in cells.
Conclusion and Significance: We conclude that of multisite phosphorylation of GLI1 by ERK2 or other MAP kinases weakens GLI1-SUFU binding, thereby facilitating GLI1 activation and contributing to both physiological and pathological crosstalk.
Syed, A, Lukacsovich, T, Pomeroy, M, Bardwell AJ, … Bardwell, L, Marsh, JL, and MacGregor, G (2019)
Miles to go (mtgo) encodes FNDC3 proteins that interact with the chaperonin subunit CCT3 and are required for NMJ branching and growth in Drosophila
Developmental Biology, 445, 37-53
Background: Analysis of mutants that affect formation and function of the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction (NMJ) has provided valuable insight into genes required for neuronal branching and synaptic growth.
Results: Miles to go (mtgo) encodes the Drosophila ortholog of vertebrate FNDC3 proteins. We show that MTGO is required for the growth and branching of motorneurons at NMJs in flies, and that it interacts genetically and physically with the chaperonin subunit CCT3.
Conclusion and Significance: These findings provide insight into the role of MTGO in neuronal function in flies and may illuminate some of the functions of FNDC3 proteins in humans. This is important as human FNDC3B protein is overexpressed in several cancers and also is associated with increased risk of glaucoma.
Bardwell, AJ, Lagunes, L, Zebarjedi, R, and Bardwell, L (2017)
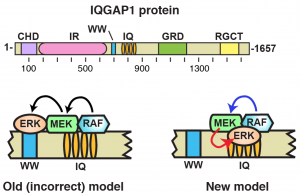
The WW domain of the scaffolding protein IQGAP1 is neither necessary nor sufficient for binding to the MAPKs ERK1 and ERK2.
J. Biol. Chem., 292: 8750-8761
Background: Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) scaffold proteins, such as IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1 (IQGAP1), are promising targets for novel therapies against cancer and other diseases.
Such approaches require accurate information about which domains on the scaffold protein bind to the kinases in the MAPK cascade.
Previous studies have suggested that the WW domain of IQGAP1 binds to the cancer-associated MAPKs ERK1 and ERK2, and that this domain might thus offer a new tool to selectively inhibit MAPK activation in cancer cells.
Results: We showed that the IQ domain of IQGAP1 is both necessary and sufficient for binding to the MAP kinases ERK1 and ERK2, as well as to the MAPK kinases MEK1 and MEK2. Furthermore, we showed that the WW domain is not required for ERK-IQGAP1 binding, and contributes little or no binding energy to this interaction, challenging previous models of how WW-based peptides might inhibit tumorigenesis.
Conclusion and Significance: These results prompt a re-evaluation of published findings and a refined model of IQGAP scaffolding.
Bardwell AJ and Bardwell, L (2015)
Two hydrophobic residues can determine the specificity of MAP kinase docking interactions.
J. Biol. Chem., 290:26661-266674
Background: MAPK cascade proteins bind to each other selectively via docking interactions.
Results: The high selectivity of JNK family MAPKs for cognate binding partners is controlled by two key hydrophobic residues in the docking site.
Conclusion: This contrasts with other proposed models of docking specificity.
Significance: This has implications for drug design and for the evolution of signaling specificity.