Disruption of β-Catenin-Dependent Wnt Signaling in Colon Cancer Cells Remodels the Microenvironment to Promote Tumor Invasion
Chen, G.T., Tifrea, D.F., Murad, R., Habowski, A.N., Lyou, Y., Duong, M.R., Hosohama, L., Mortazavi, A., Edwards, R.A., Waterman, M.L.. Disruption of β-Catenin-Dependent Wnt Signaling in Colon Cancer Cells Remodels the Microenvironment to Promote Tumor Invasion. Molecular Cancer Research. 2022 March 1; 20(3):468-484. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786

Fig. 1. Decreasing Wnt in SW480 and SW620 colon cancer xenografts increases cell migration and invasion.
Transcriptomic and proteomic signatures of stemness and differentiation in the colon crypt
Habowski, A.N., Flesher, J.L., Bates, J.M., Tsai, C.F., Martin, K., Zhao, R., Ganesan, A.K., Edwards, R.A., Shi, T., Wiley, H.S., Shi, Y., Hertel, K.J., Waterman, M.L. Transcriptomic and proteomic signatures of stemness and differentiation in the colon crypt. Communications Biology 3. 2020 Aug 19; 3(1):453. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01181-z
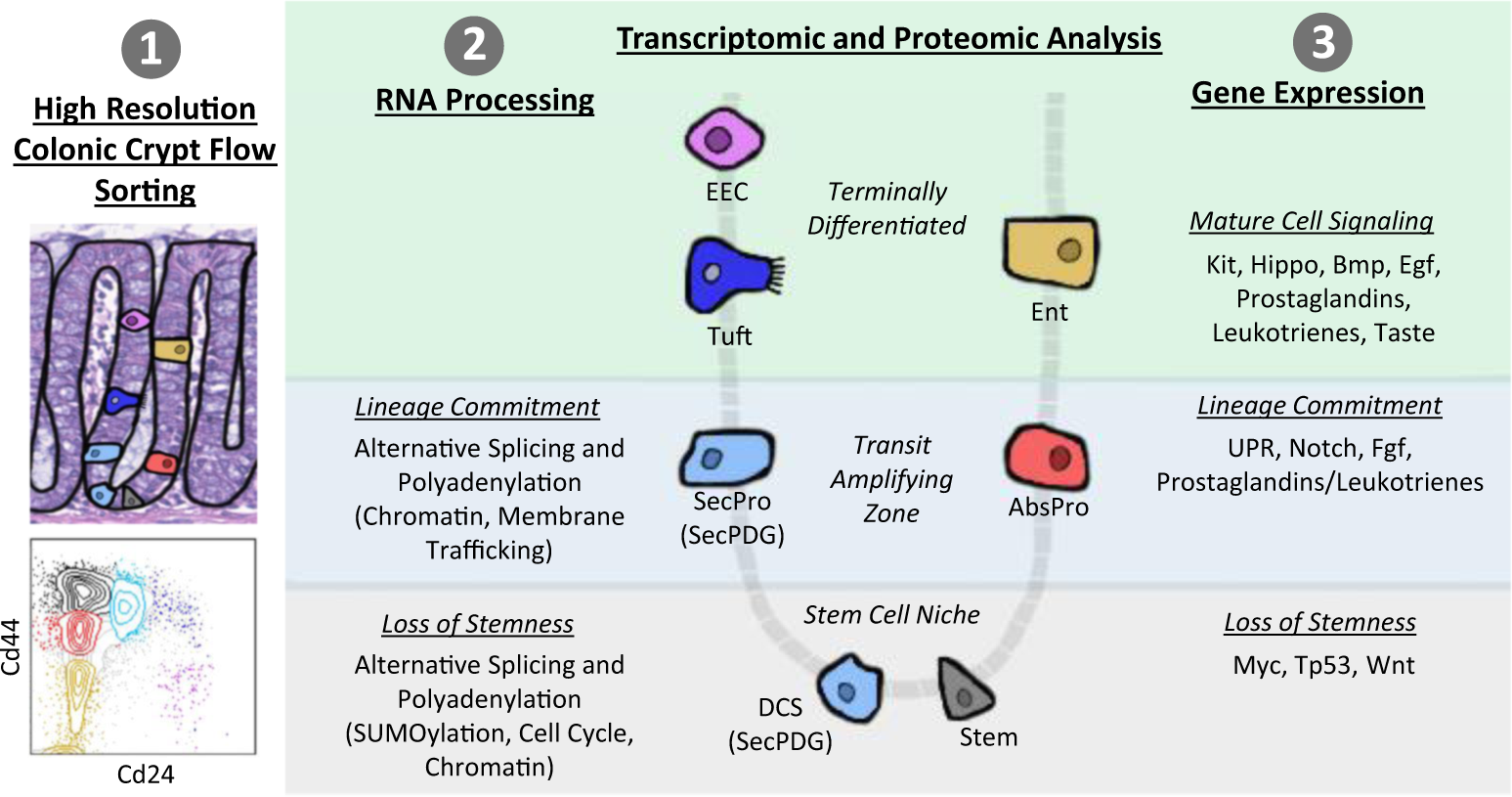
Fig. 8: Summary of transcriptome and proteome changes in colon crypt homeostasis.
Mathematical modeling links Wnt signaling to emergent patterns of metabolism in colon cancer
Lee, M., Chen, G.T., Puttock, E., Wang, K., Edwards, R.A., Waterman, M.L., Lowengrub, J. Mathematical modeling links Wnt signaling to emergent patterns of metabolism in colon cancer. Molecular Systems Biology. 2017 Feb 9; 13(2):912. doi: 10.15252/msb.20167386
Synopsis: A self-organizing spotted pattern of glycolysis is discovered in xenograft colon tumors and is consistent with a Turing reaction–diffusion system. Model predictions of gene expression and therapy are validated and reveal synergistic outcomes by targeting Wnt and the glycolytic cell population.
Inhibition of nuclear Wnt signalling: challenges of an elusive target for cancer therapy
Lyou, Y., Habowski, A.N., Chen, G.T., Waterman, M.L. Inhibition of nuclear Wnt signalling: challenges of an elusive target for cancer therapy. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2017 Dec; 174(24):4589-4599. doi: 10.1111/bph.13963

Fig. 2. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the Wnt enhancesosome.
Lactate/pyruvate transporter MCT-1 is a direct Wnt target that confers sensitivity to 3-bromopyruvate in colon cancer
Lactate/pyruvate transporter MCT-1 is a direct Wnt target that confers sensitivity to 3-bromopyruvate in colon cancer. Cancer Metab. 2016 OCt 3;4:20. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0159-3
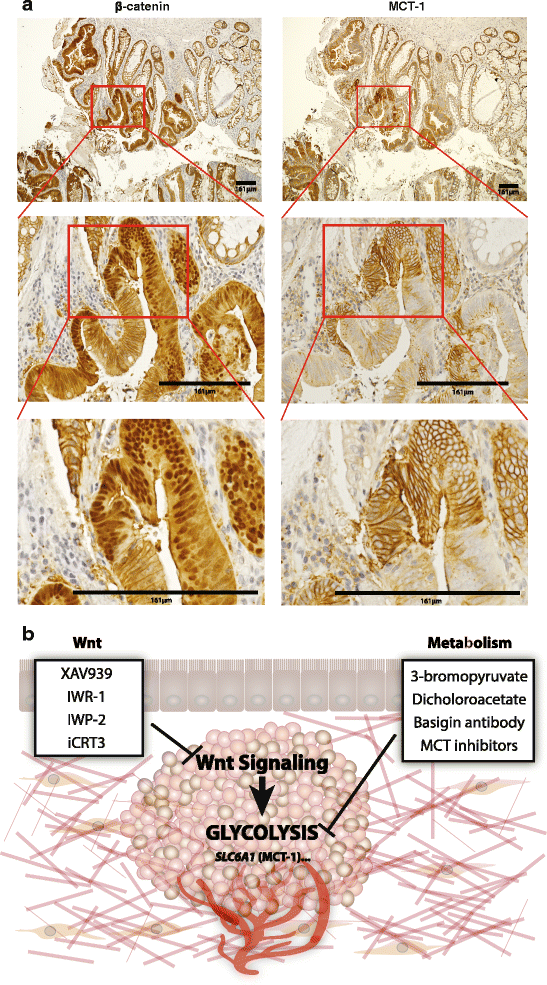
Fig. 7. Wnt signaling influences cancer metabolism through regulation of SLC16A1/MCT-1 expression.
Cancer: leaping the E-cadherin hurdle
Chen, G.T. and Waterman, M.L. Cancer: leaping the E-cadherin hurdle. The EMBO Journal. 2015 Sep 14; 34(18): 2307-2309. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592757
Fig. 1. E-cadherin levels and β-catenin availability in tumors.
Wnt signaling directs a metabolic program of glycolysis and angiogenesis in colon cancer
Pate, K.T., Stringari, C., Sprowl-Tanio, S., Wang, K., TeSlaa, T., Hoverter, N.P., McQuade, M.M., Garner, C., Digman, M.A., Teitell, M.A., Edwards, R.A., Gratton, E., Waterman, M.L. Wnt signaling directs a metabolic program of glycolysis and angiogenesis in colon cancer. The EMBO Journal. 2014 Jul 1; 33(13):1454-73. doi: 10.15252/embj.201488598
Fig. 6. Blocking Wnt reduces in vivo tumor growth.
Fig. 8. Wnt promotes aerobic glycolysis through PDK1.
TCF/LEFs and Wnt Signaling in the Nucleus
Cadigan, K.M. and Waterman, M.L. TCF/LEFs and Wnt Signaling in the Nucleus. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 2012 Nov 1; 4(11):a007906. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007906
Fig. 3. Regulation of TCF/LEFs in invertebrates and vertebrates.
The TCF C-clamp DNA binding domain expands the Wnt transcriptome via alternative target recognition
Hoverter, N.P., Zeller, M.D., McQuade, M.M., Garibaldi, A., Busch, A., Selwan, E.M., Hertel, K.J., Baldi, P., Waterman, M.L. Nucleic Acids Research. 2014 Dec 16; 42(22):13615-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1186

Fig. 3. The C-clamp binds to Helper sites on a genome-wide scale.
Dr. Waterman’s Publications: GoogleScholar
Collaborations
————
Disruption of the circadian clock drives Apc loss of heterozygosity to accelerate colorectal cancer

Spatial transcriptomics using combinatorial fluorescence spectral and lifetime encoding, imaging and analysis
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27798-0
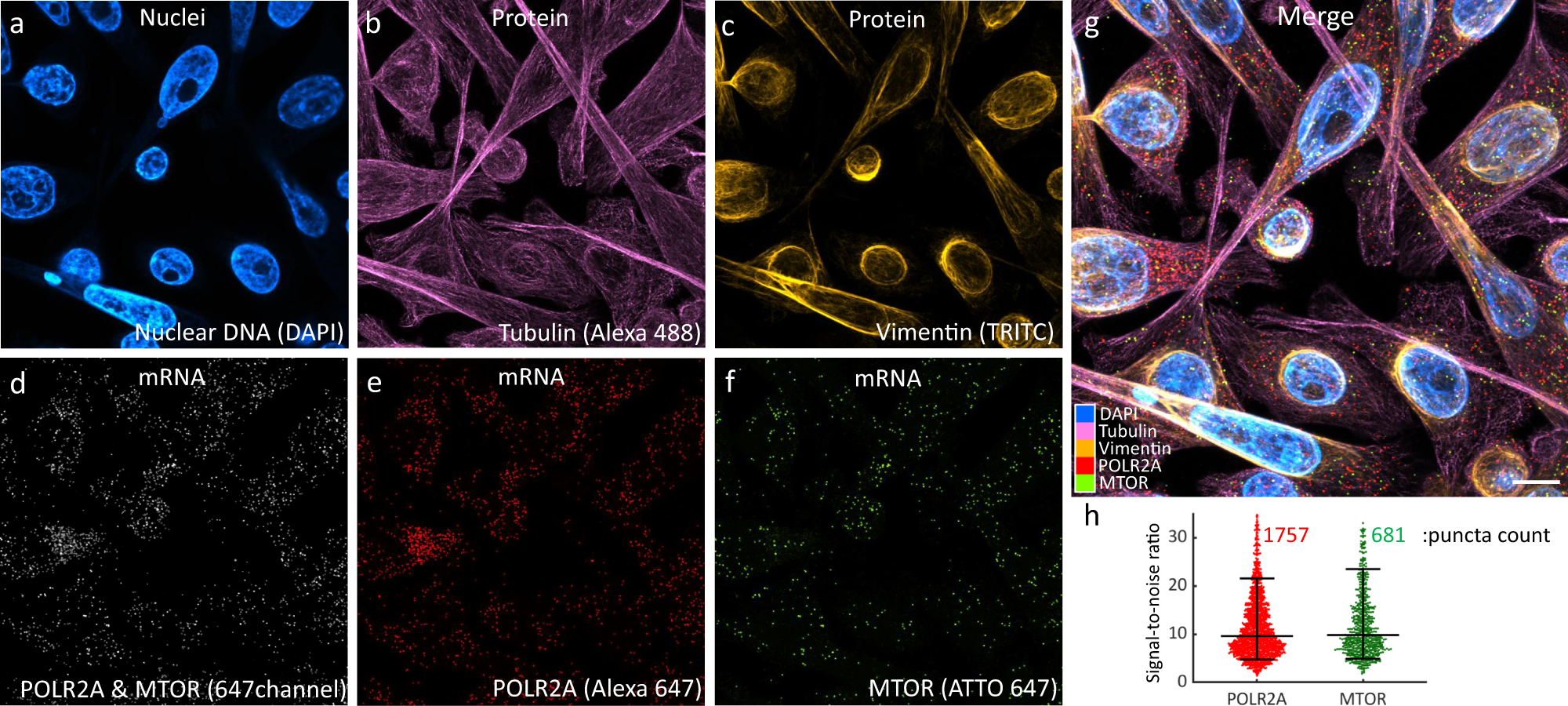
Fig. 6. Simultaneous 4-plex co-detection of protein and mRNA in colorectal cancer SW480 cells.
An in vitro vascularized micro-tumor model of human colorectal cancer recapitulates in vivo responses to standard-of-care therapy
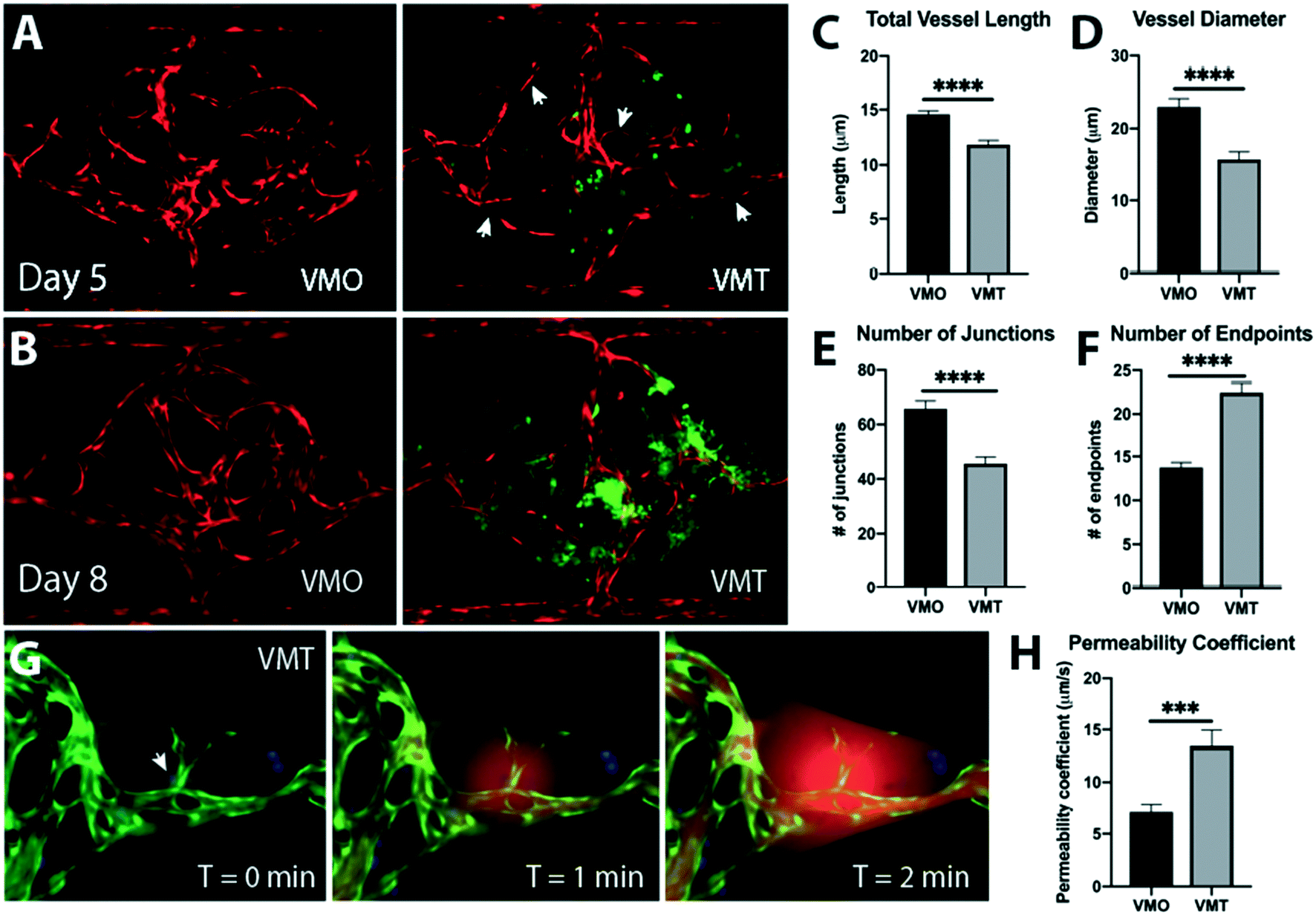
Fig. 2 The VMT models key features of in vivo tumor vasculature.
α-Ketoglutarate attenuates Wnt signaling and drives differentiation in colorectal cancer
Tran, T.Q., Hanse, E.A., Habowski, A.N., Li, H., Ishak Gabra M.B., Yang, Y. Lowman, X.H., Ooi, A.M., Liao, S.Y., Edwards, R.A., Waterman, M.L., Kong, M. Nature Cancer. 2020 Mar; 1(3):345-358. doi: 10.1038/s43018-020-0035-5
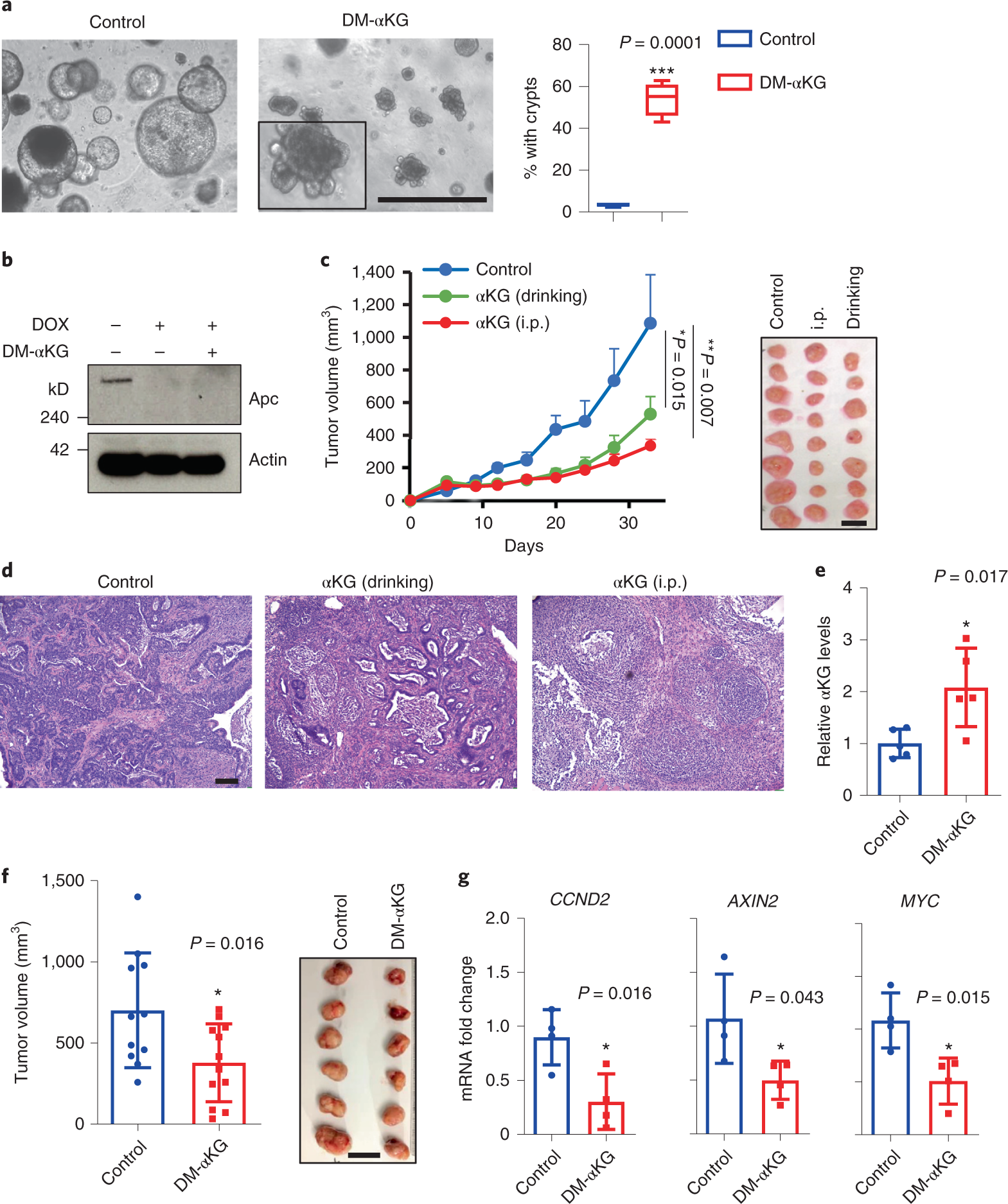
Fig. 6: αKG supplementation inhibits the growth of highly mutated CRC tumors in vivo.
Differential Effects of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Isoforms on Tumor Growth and T-Cell Factor 4/AP-1 Interactions in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
Vuong, L.M., Chellappa, K., Dhahbi, J.M., Deans, J.R., Fang, B., Bolotin, E., Titova, N.V., Hoverter, N.P., Spindler, S.R., Waterman, M.L., Sladek, F.M. Molecular and Cell Biology. 2015 Oct; 35(20):3471-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00030-15

Fig. 11. Model of HNF4α, TCF4, and AP-1 interplay in HCT116 human colon cancer cells.