Professor Roger H. Rangel
Assistant Specialist: Xiaoli Bian
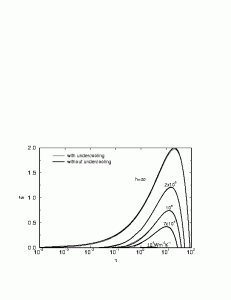
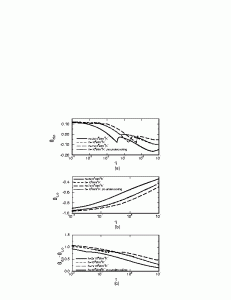
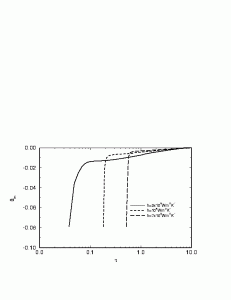
The inviscid stagnation-flow solidification problem is studied numerically including the effect of contact resistance and undercooling during solidification. In addition, the long-time behavior of the process is studied with an analytical method. The effect of contact resistance at the initial liquid-solid contact plane is demonstrated by comparing the solidification behavior for cases with different contact heat transfer coefficient. The effect of undercooling is examined by comparing model predictions including this effect with those obtained when equilibrium solidification with interface temperature at the thermodynamic equilibrium temperature is used. The study shows that undercooling delays the start of solidification but has a negligible effect on the long time behavior of the process. A sufficiently large contact resistance may prevent solidification when undercooling is included in the model. At late stages when substrate remelting occurs, the analytical solution for the long-time behavior of the process indicates that remelting of the substrate proceed at a constant velocity.
References
- Rangel, R., Bian, X. (1998). “Undercooling and Contact Resistance in Stagnation-Flow Solidification on a Semi-Infinite Substrate”. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 41(12), 1645-1653.
Figures