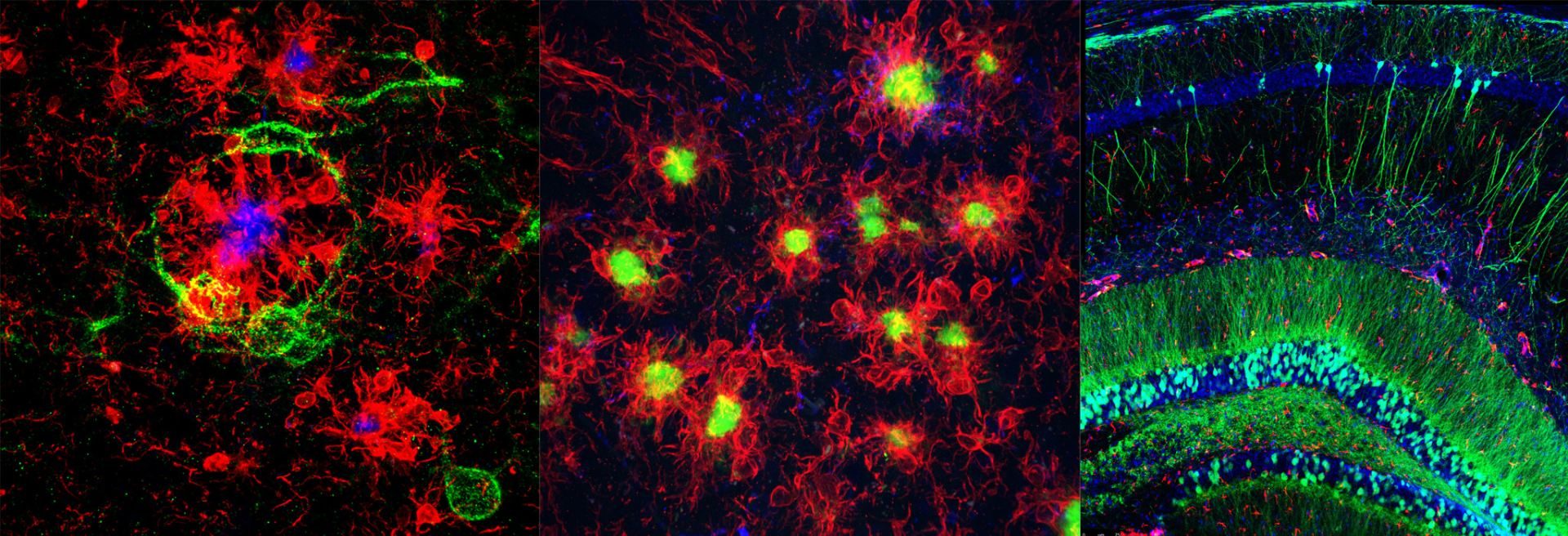
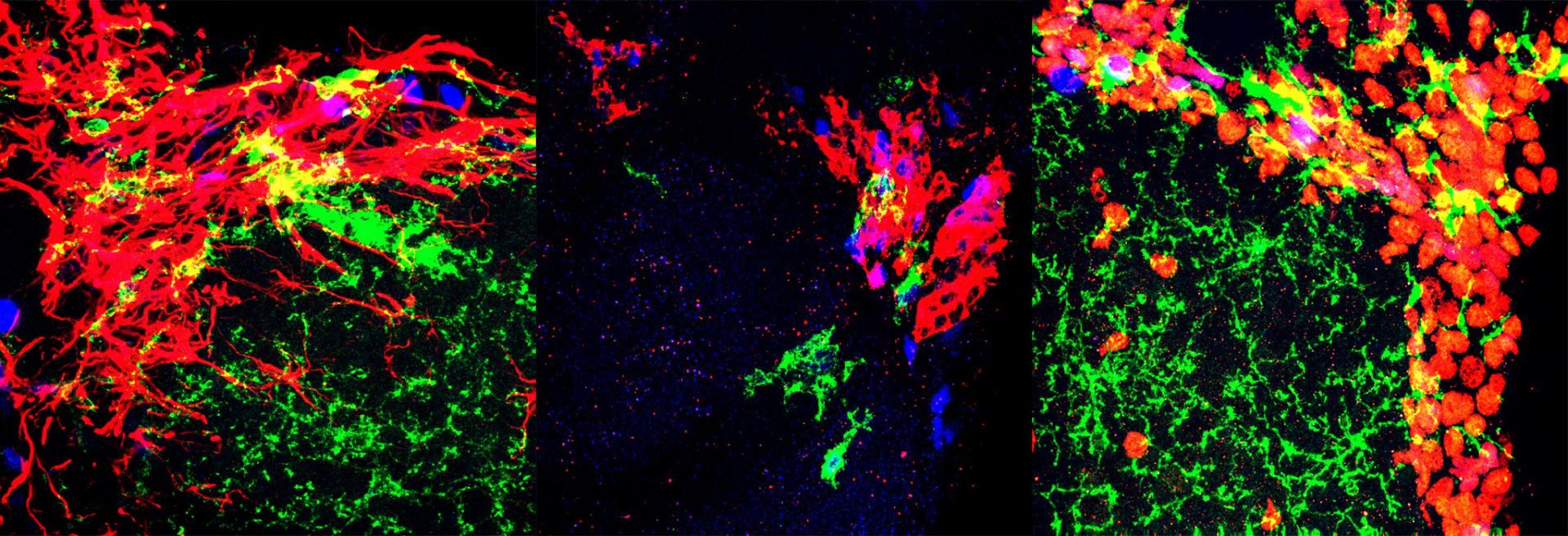
Microglia in the healthy and diseased brain
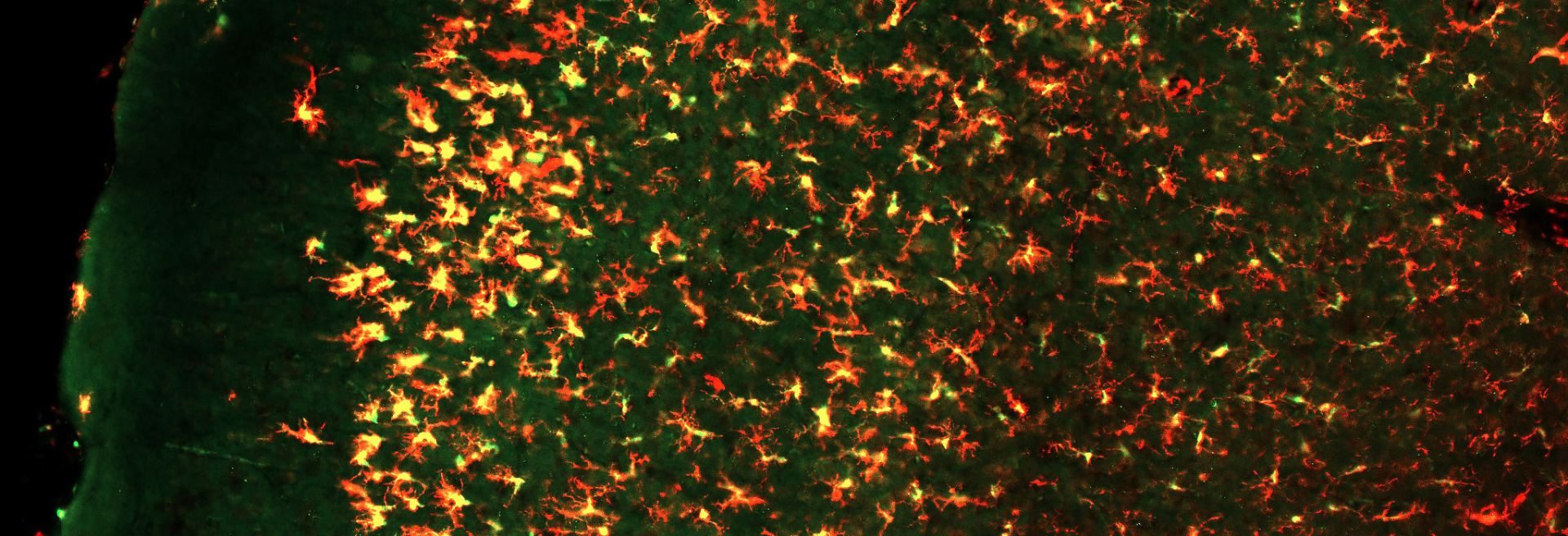
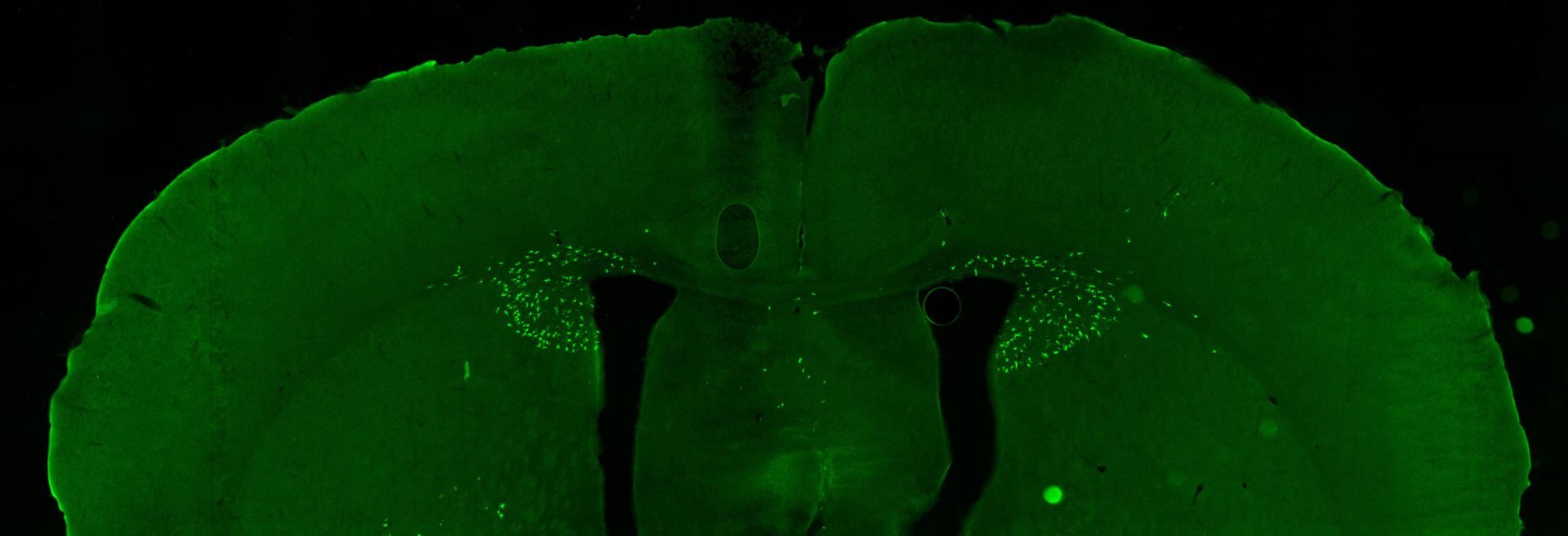
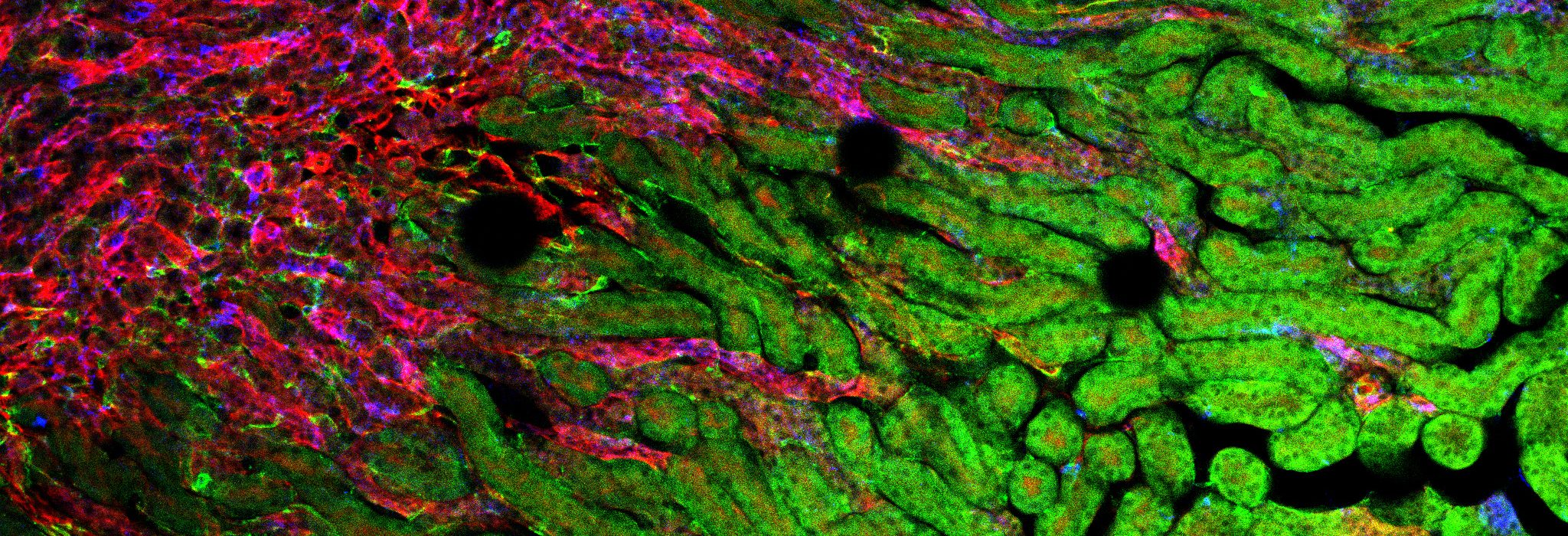
We are interested in understanding the roles of microglia in the homeostatic brain, as well as their contributions to disease and injury, particularly in Alzheimer’s disease. We have developed approaches to deplete the microglial population via dietary administration of CSF1R inhibitors, and through their elimination we can gain insight into their roles.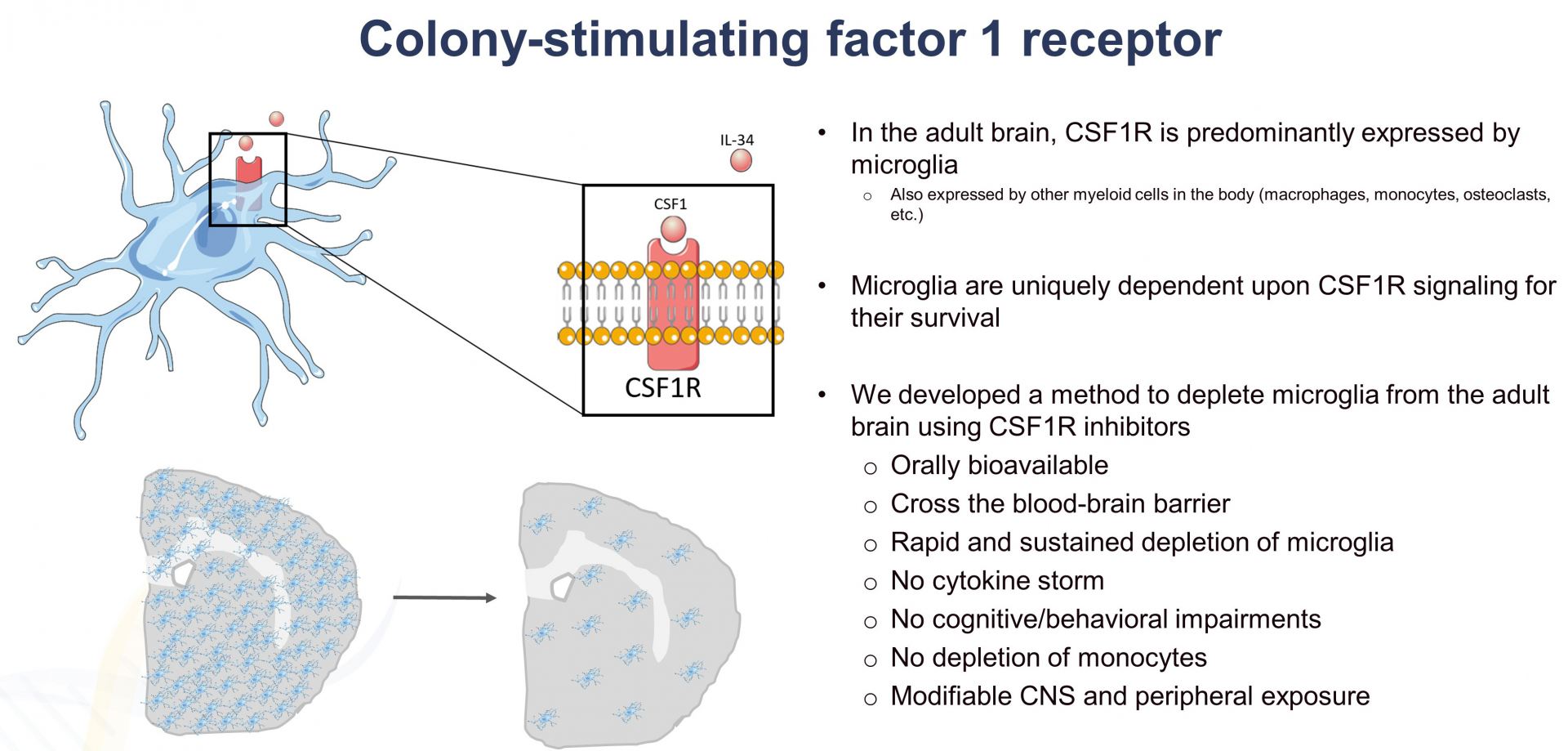
For details on our latest studies please head to the Publications page, where our papers can be downloaded.
If you are interested in exploring gene expression from our studies then please click here. Our datasets are fully searchable and allow the user to see how gene expression changes in various disease models, and how the absence of microglia effects things. Many datasets are also available to explore microglial repopulation, repopulation from White Matter/SVZ microglia, or from brains where we replace the microglia with monocytes.
Animal Models of Alzheimer’s disease
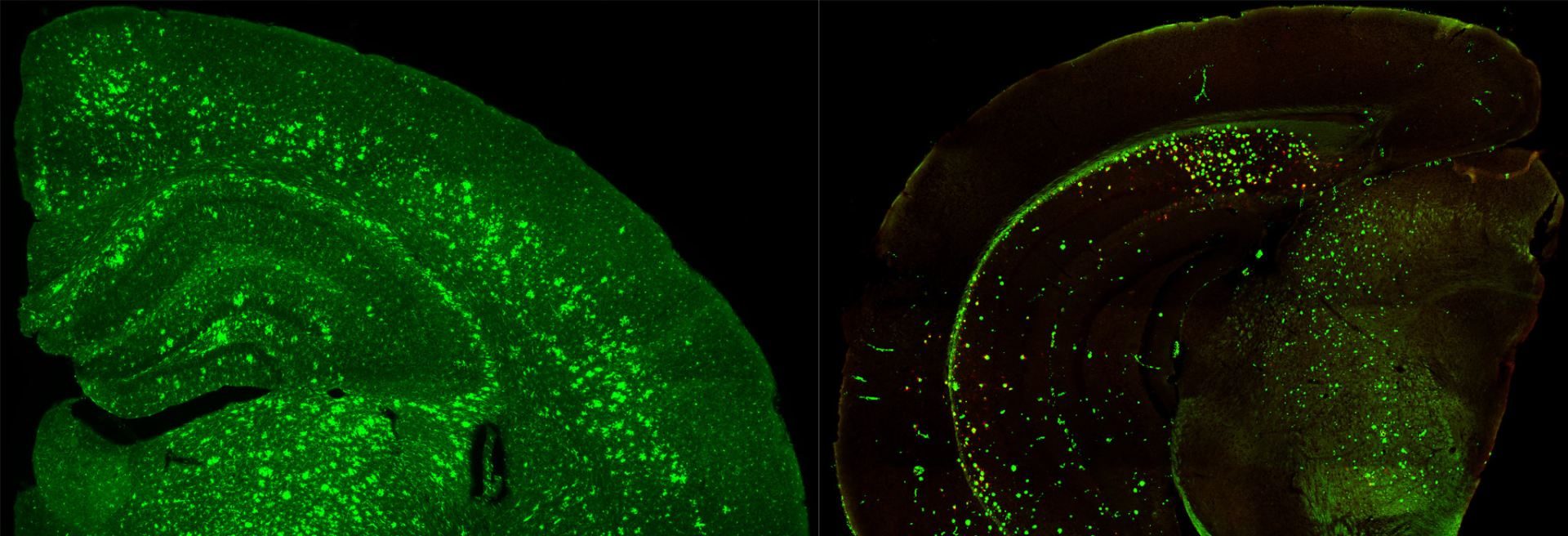
We are also part of the NIA funded MODEL-AD consortium (Model Organism Development and Evaluation for Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease) and work to produce new mouse models and then phenotype them across their lifespans. Mouse models are based on humanisation of key genes (i.e., Aβ, Tau), and are combined with GWAS and exome-identified risk variants from human populations. All mice and data are freely available from The Jackson Labs, and the AD Knowledge Portal, respectively.
On this website we have several gene expression datasets that can be explored in an interactive fashion, including timecourses from 5xFAD, 3xTg-AD, and hAβ-KI mice. In addition, we have datasets on the impact of genetic diversity on gene expression in 5xFAD mice, as well as GWAS identified risk variants such as Trem2*R47H. Click here to access.
The Green Lab